Abstract:
This investigation used the antimicrobial proteins found in moringa oleifera seeds to substantially decrease the parts per million (PPM) of polluted water. Nine containers of contaminated water were treated with this extract to filter hazardous particulates. A TDS meter was used to determine the PPM of the containers with zero, three, and six seeds. The data supported the hypothesis that the moringa seed extract would purify contaminated water.
Introduction:
Moringa oleifera is a plant that was introduced to the Caribbean and parts of Africa during Indian indentured servitude. The positively charged extract from its seed acts as a coagulant and an antimicrobial agent, allowing it to better adhere to negatively charged particles from threatening substances. This then results in bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, located within contaminated water to sink to the bottom to be filtered out, leaving purified water.
Experimental details:
A total dissolved solids (TDS) meter was used throughout this investigation to measure the parts per million (PPM) of the water, indicating the purity level. The contaminated water initially had a PPM of 600, which is considered to be severely unfit for human consumption but yet is seen as a drinking source in many countries. The seeds were crushed into a power-like substance, which was then added to the nine containers of contaminated water. The first three containers were not given any seeds, the second three had the extract of three seeds, and the third three had the extract of six seeds. The water was left for two hours, with data being recorded throughout. The particulates and bacteria that accumulated and deceased had sunk and were filtered out using a cloth.
Results and discussion:
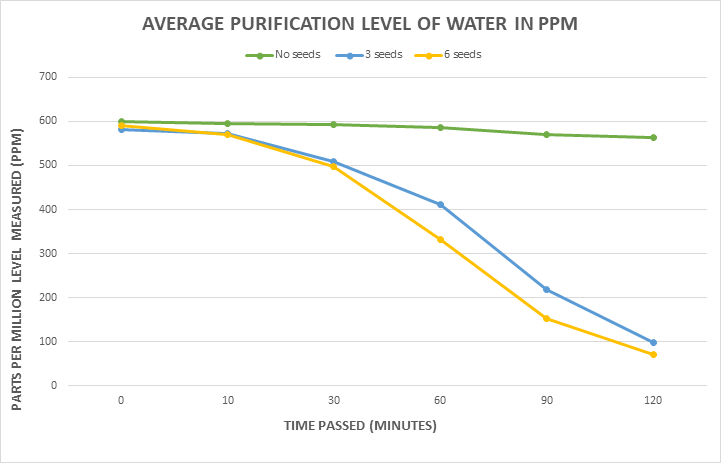
After conducting this experiment, the containers of water were all measured using the TDS meter for levels of PPM. The containers with no seeds averaged a 564 PPM, three seeds with 99 PPM, and six seeds with 72 PPM. Levels under 100 PPM are desirable and fit for human consumption. Ultimately, the contaminated water was able to go from a disturbing concentration to be safer and more purified. The extract can isolate any containments in water that are harmful, causing the water to increase in quality. This is an inexpensive way to purify water which can save millions of lives as it immobilizes the consumption of any diseases or micro-organisms. This procedure can be used globally, especially in parts without clean water.
Conclusion:
The results demonstrate that tremendous changes did occur within the PPM levels of the contaminated water, after adding the moringa seed extract. According to the World Health Organization, two billion people die globally each year from drinking contaminated water, with the lead in countries that do not have sources to clean water. Regardless of bacteria, items such as pesticides or fertilizer may additionally have great consequences in the case which they enter the water. Essentially, with global warming increasing as a result of such activities and countries become more polluted, the demand for clean water rises. This investigation proposes a way to drastically lower the PPM of contaminated water. The outcome of this study can advance our understanding of the moringa oleifera seed with results that can save lives.
Acknowledgments:
I would like to thank Erin Cernuda for offering me the opportunity to conduct this research and Eric Castaing for guiding me through this study.
Figure 1: Table demonstrating the data collected throughout the experiment.
|
|
Initial PPM
|
10 minutes
|
30 minutes
|
1 hour
|
1 hour & 30 minutes
|
2 hours
|
|
1a (no seeds)
|
602
|
600
|
597
|
589
|
572
|
567
|
|
1b (no seeds)
|
596
|
594
|
591
|
586
|
573
|
569
|
|
1c (no seeds)
|
601
|
593
|
589
|
588
|
569
|
556
|
|
Average
|
599
|
595
|
592
|
587
|
571
|
564
|
|
2a (3 seeds)
|
581
|
572
|
511
|
422
|
255
|
103
|
|
2b (3 seeds)
|
592
|
584
|
509
|
410
|
201
|
99
|
|
2c (3 seeds)
|
574
|
563
|
505
|
401
|
200
|
96
|
|
Average
|
582
|
573
|
508
|
411
|
218
|
99
|
|
3a (6 seeds)
|
563
|
540
|
483
|
227
|
108
|
62
|
|
3b (6 seeds)
|
617
|
598
|
503
|
393
|
196
|
83
|
|
3c (6 seeds)
|
595
|
576
|
506
|
376
|
154
|
71
|
|
Average
|
591
|
571
|
497
|
333
|
152
|
72
|
Figure 2: Graph showing the significant decrease in PPM and increase in purity level with the containers having the seed extract.
References:
6 Science-Based Health Benefits of Moringa oleifera. (2018, May 4). Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/6-benefits-of-moringa-oleifera
Moringa: Benefits, side effects, and risks. (2020, January 2). https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319916
Bacteria and viruses commonly found in drinking water. (2014, July 31). Water Tech Online. https://www.watertechonline.com/wastewater/article/15545721/bacteria-and-viruses-commonly-found-in-drinking-water
US EPA, O. (2017, November 2). Drinking Water [Reports and Assessments]. US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/report-environment/drinking-water
A How-To Guide to Purifying Water with Moringa Seeds at Home. (2015, March 26). Dead Sea Moringa. http://www.deadseamoringa.com/a-how-to-guide-to-purifying-water-with-moringa-seeds-at-home/
Drinking-water. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water
Nations, U. (n.d.).
Water. United Nations; United Nations. Retrieved from
https://www.un.org/en/global-issues/water



